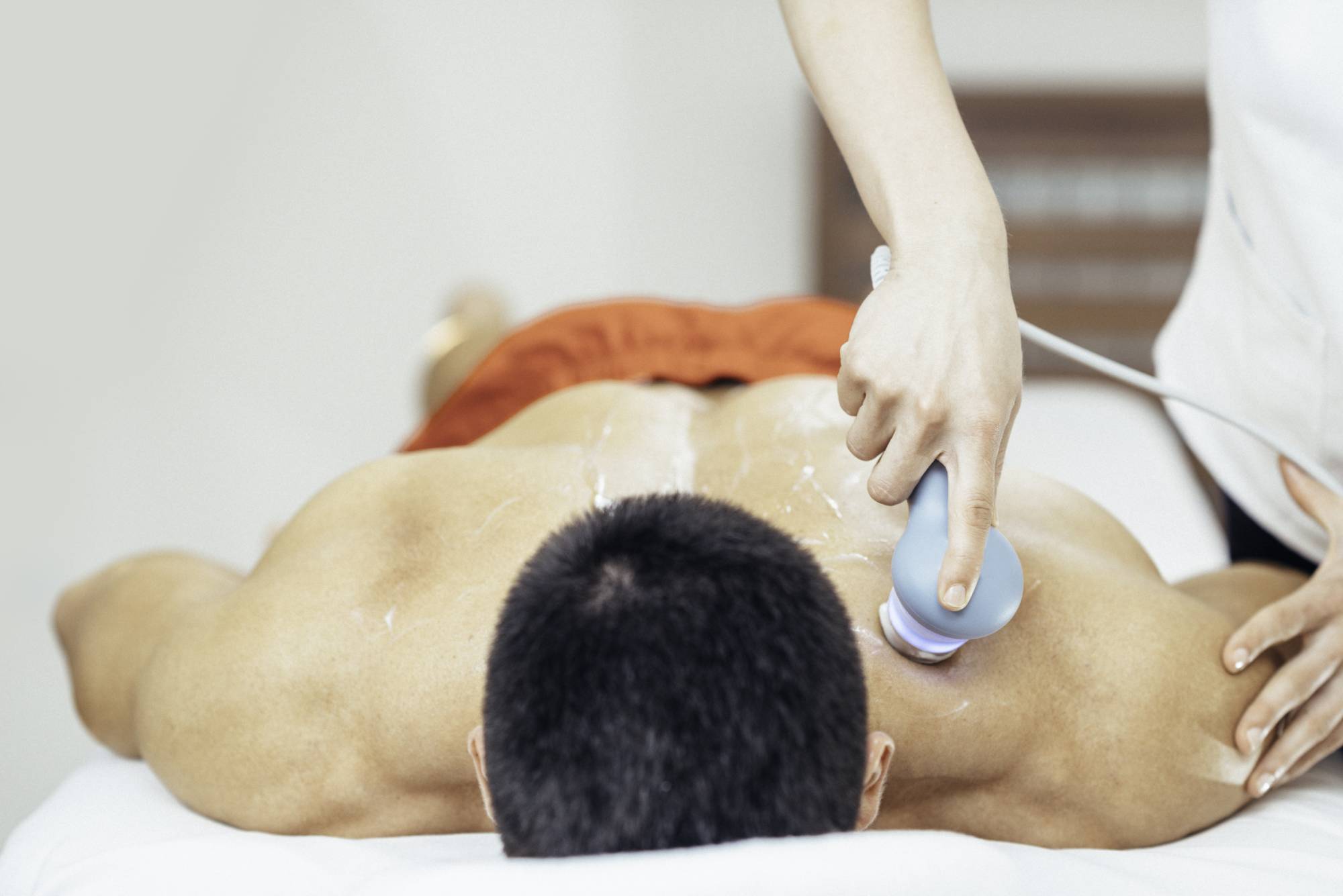
Overview
Ultrasound can be used therapeutically to provide deep heating to soft tissues in the body, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints. Deep heating results in improved elasticity and range of motion, as well as decreased pain. The non-thermal effects of this technique are modulating microscopic gas bubbles in tissues and generating movement in fluid within tissues, both of which lead to increased cellular activity.
During ultrasound therapy, a physical therapist uses an ultrasound device to apply high-frequency sound waves to the body, transferring energy in the form of vibrations. These vibrations occur faster than heard or felt by humans, though patients may experience mild warming or tingling sensations in the targeted region. This energy transfer is what produces deep heating and fluid changes.
Benefits
Ultrasound therapy translates mechanical energy into therapeutic benefits in the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions. Physical therapists can determine the depth of penetration and intensity of the ultrasound waves based on each patient’s needs. Benefits of this treatment include:
- Deep heating to soft tissues
- Reduced pain
- Increased tissue elasticity and range of motion
- Increased circulation, which promotes healing
- Treatment of inflammation, such as in bursitis, tendonitis, arthritis, and sprains
- Treatment of joint problems, such as frozen shoulder and stiff joints
- Treatment of muscle strains
Contraindications
Ultrasound therapy is generally contraindicated during pregnancy. In addition, it should not be used over open wounds or fractures, an active area of cancer, or an area with metal implants or a pacemaker.
