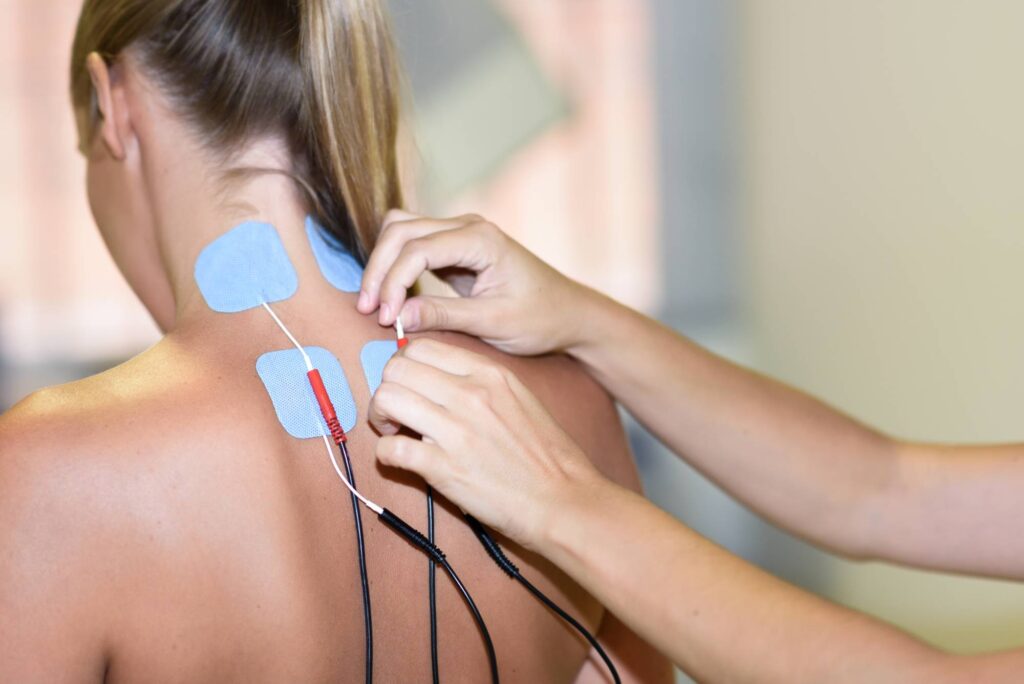
Overview
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation is a technique that uses electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contraction or modulate nerves in a target region. The physical therapist places electrodes onto the skin, which applies an electric current to the underlying muscle and/or nerve.
For muscular electrical stimulation, the goal is to mimic the natural way the body activates its muscles; repeated muscle contractions then improve muscular function and health. This technique can be especially useful in situations of muscle weakness or stroke rehabilitation.
Electrical stimulation can also target muscle spasms and pain. In this case, the goal is to apply an electrical current to the nerve that is causing discomfort and modulating its activity.
Benefits
Electrical stimulation is a versatile therapy that interacts with the electrical signals that naturally occur in the body’s nervous system and neuromuscular junctions. It can mimic normal impulses and to correct dysfunction. Benefits of electrical stimulation therapy include:
- Reducing acute and chronic pain
- Improving circulation
- Promoting tissue repair
- Decreasing muscle spasm
- Strengthening and/or retraining muscles
Contraindications
Because this therapy applies an electric current to the body, it should not be used in the presence of an implanted electrical device, such as a pacemaker or spinal cord stimulator, to avoid interference. In general, electrical stimulation should be used on healthy skin, avoiding sensitive areas like the eyes, throat, or wounds. The most common side effect is mild skin irritation at the electrode site.
